This is an old revision of the document!
BioNTech
Development of mRNA Vaccine Technology
On October 16, 2019, Nature published an article describing BioNTech's successes in testing experimental immunotherapy vaccines for cancer, and suggested the progress could be applied to solve problems like rabies and pandemic influenza.1)
Clinical Trials Pfizer May 2, 2022 FOIA
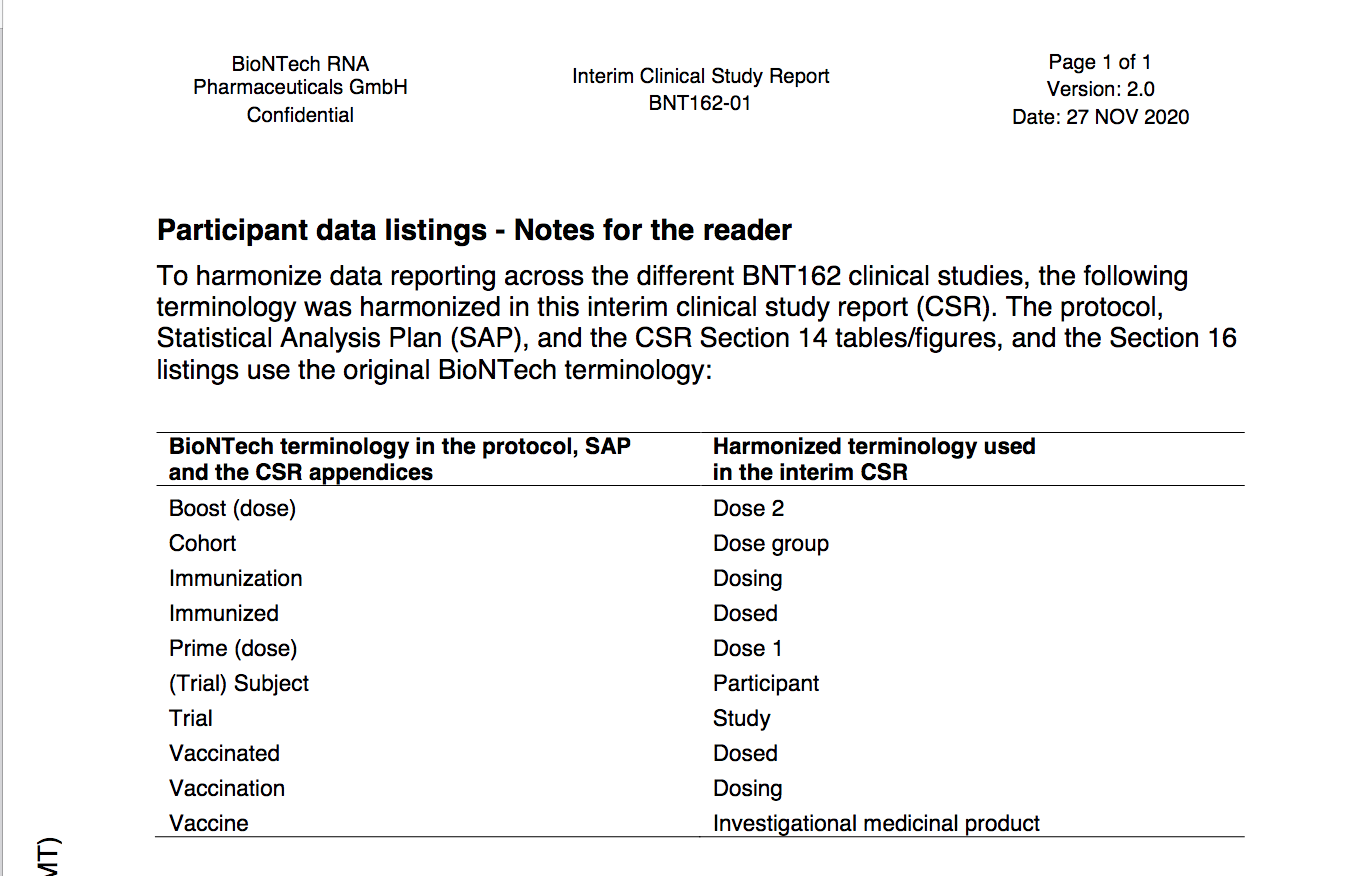
Definitions COVID Vaccine - Investigational medicinal product2)
Sponsors & Signatures
Trial Investigators Master File
Deluxe CV bios for all 3)
Sponsor trial sign off 4)
sponsor personnel 5)
Dr Stephen Thomas MD study 6)
coordinating 7)
BioNTech RNA Pharmaceuticals GmbH Confidential Interim Clinical Study Report
BNT162-01 Page 1 of 1 Version: 2.0 Date: 26 Nov 2020 8)
16.1.13
List of sponsor personnel who materially affected the trial conduct The following table presents a list of sponsor personnel who materially affected the trial conduct. The full list of all involved sponsor personnel is maintained in the trial master file 9)
- Name Role
- Özlem Türeci, MD Chief Medical Officer (Sponsor’s medically qualified person) b
- Svetlana Shpyro, MD Medical Expert
- Dr. Stefan Liebscher Biostatistician (External BioNTech Consultant)
- Sean Murphy Biostatistician (External BioNTech Consultant)
- Dr. Christopher Marshallsay Head Scientific-Medical Writing a
- Dr. Frans van Huizen Senior Scientific / Medical Writer
- Dr. David Langer Clinical Study Manager
- Dr. Stefanie Bolte Clinical Study Manager
- Martin Bexon, MD Medical Monitor (External BioNTech Consultant)
- Amélie Caneparo Pharmacovigilance Manager
- Claudia Müller Clinical Data Manager (External BioNTech Consultant)
- Dr. Tania Palanche Senior Clinical Data Manager
a) Document owner fulfills the requirements of the author according to ICH E3.
b) Corresponds to the medical officer defined in ICH E3. 10)

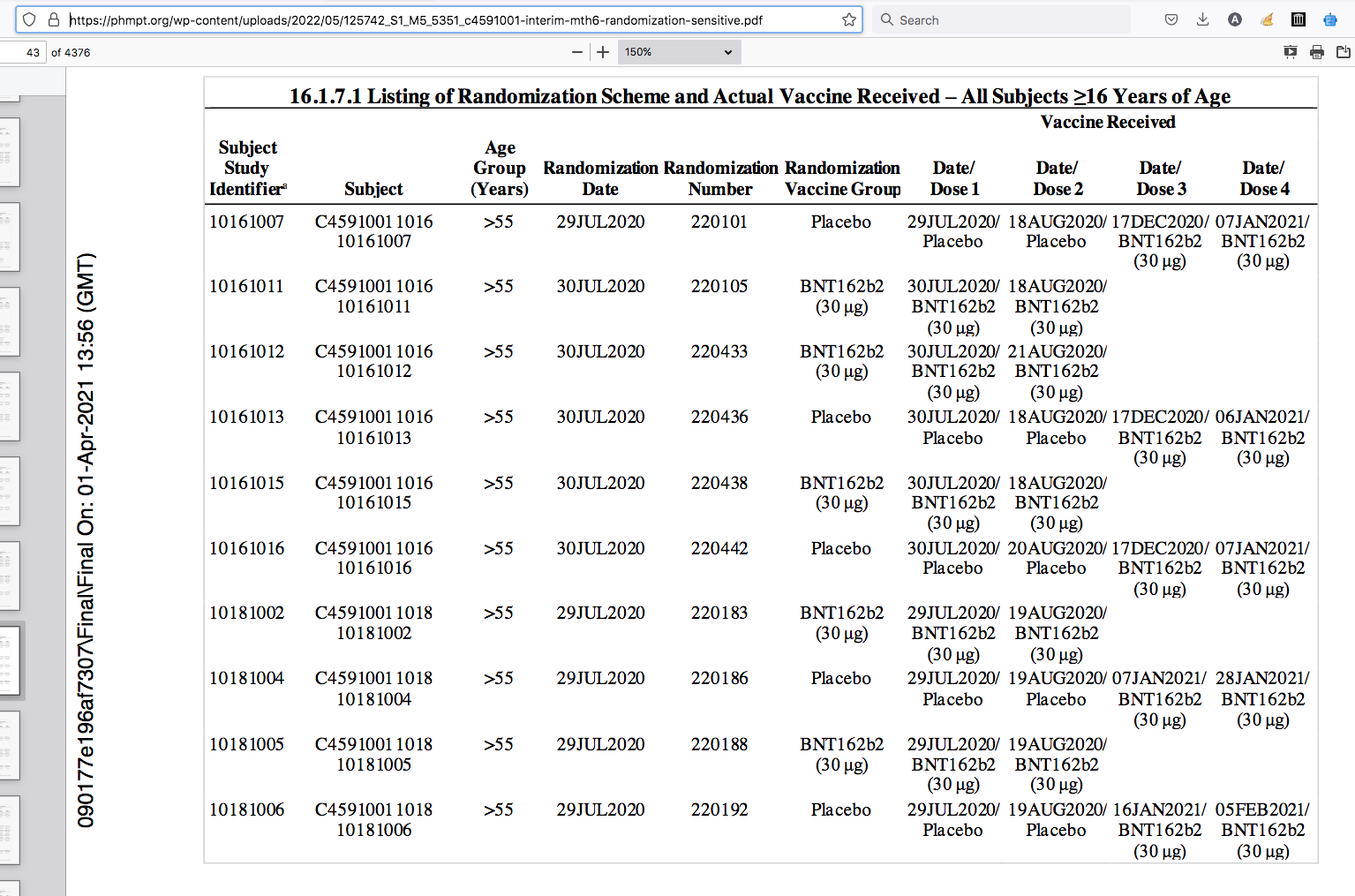
Destroying BNT162b2 Placebo Group In 180 days
Random sample - vaccine dates are squished together above dose type BNT162b2 or Placebo.
11)
Adverse Events
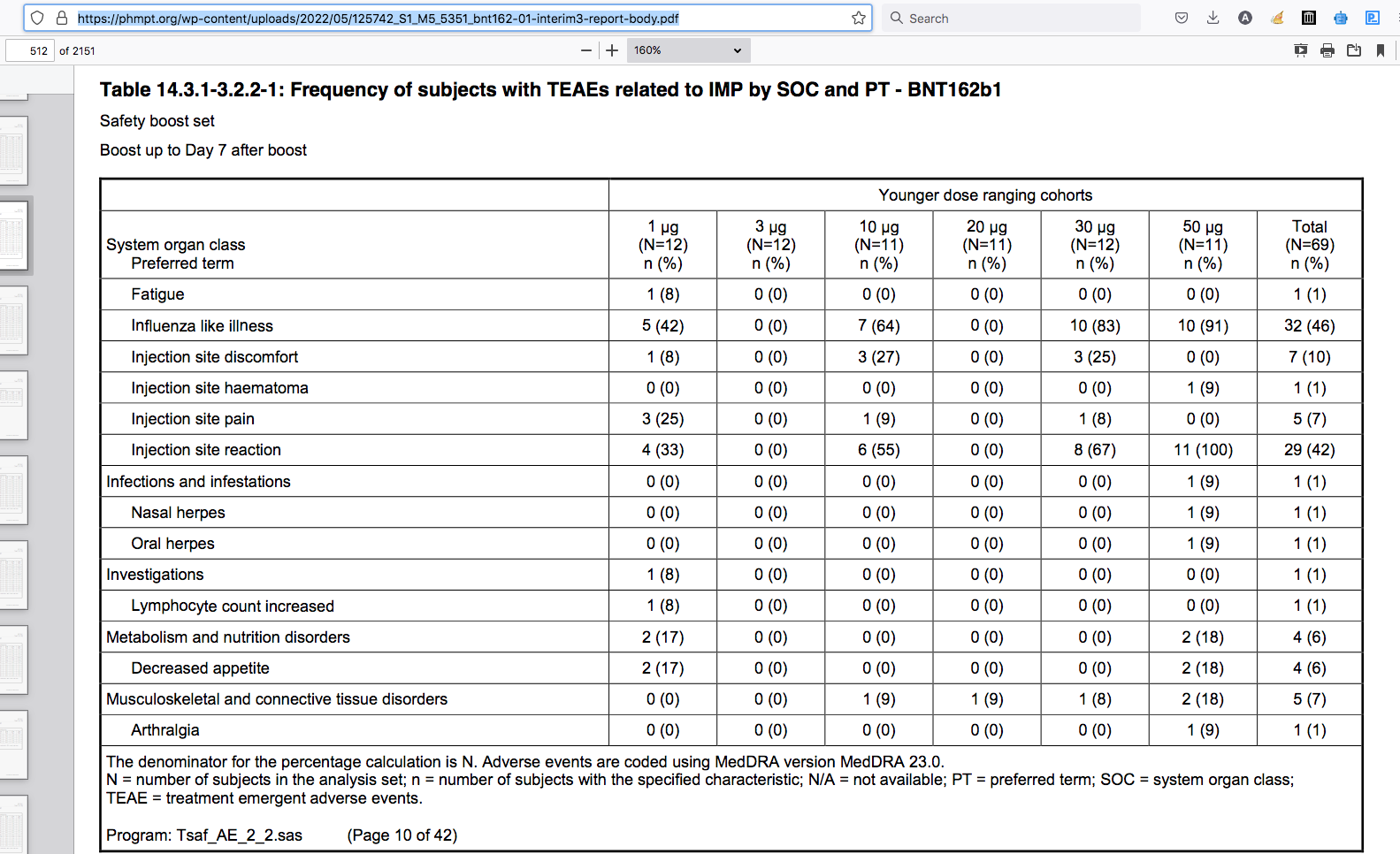
BioNTech RNA Pharmaceuticals GmbH / Tables - 6. Snapshot All TLFs Final 1.0 BNT162b1 BNT162-01 Created on 20NOV2020 Staburo GmbH. Based on clean SDTM data received on 03NOV2020. Data cut-off: 23OCT2020. Table 14.3.1-3.2.2-1: Frequency of subjects with TEAEs related to IMP by SOC and PT - BNT162b1
pdf page 512/215112)
REFERENCES
page 140/2151 - REFERENCES13) Boraschi D, Del Giudice G, Dutel C, et al. Ageing and immunity: addressing immune senescence to ensure healthy ageing. Vaccine 2010; 28(21): 3627-31.
Destexhe E, Prinsen MK, van Schöll I, et al. Evaluation of C-reactive protein as an inflammatory biomarker in rabbits for vaccine nonclinical safety studies. J Pharmacol
Toxico. Methods 2013; 68: 367-73.
Doener F, Hong HS, Meyer I, et al. RNA-based adjuvant CV8102 enhances the immunogenicity of a licensed rabies vaccine in a first-in-human trial. Vaccine 2019; 37: 1819-26.
Kamphuis E, Junt T, Waibler Z, et al. Type I interferons directly regulate lymphocyte recirculation and cause transient blood lymphopenia. Blood 2006; 108: 3253-61.
Mulligan M, Lyke KE, Kitchinet N, et al. Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 2020; 586(7830): 589-93.
Taylor DN, Treanor JJ, Sheldon EA, et al. Development of VAX128, a recombinant hemagglutinin (HA) influenza-flagellin fusion vaccine with improved safety and immune response. Vaccine 2012; 30: 5761-9.
Tsai MY, Hanson NQ, Straka RJ, et al. Effect of influenza vaccine on markers of inflammation and lipid profile. J Lab Clin Med. 2005; 145: 323-7.
US FDA Guidance for Industry - Toxicity Grading Scale for Healthy Adult and Adolescent Volunteers Enrolled in Preventive Vaccine Clinical Trials.
Walsh EE, Frenck R, Falsey AR, et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383(25): 2439-50.14)
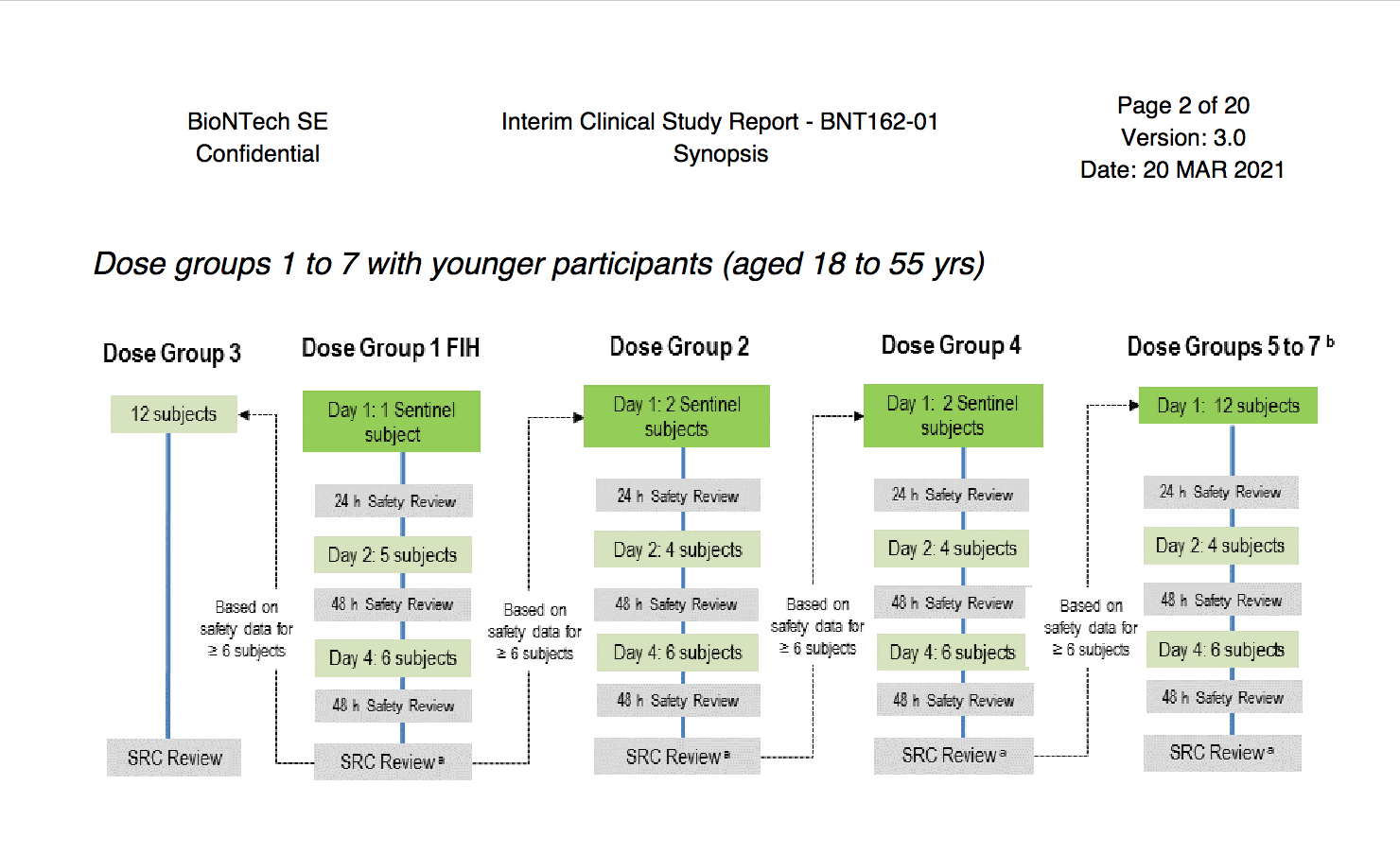
TRIAL Size and Endpoints
Possible Concerns
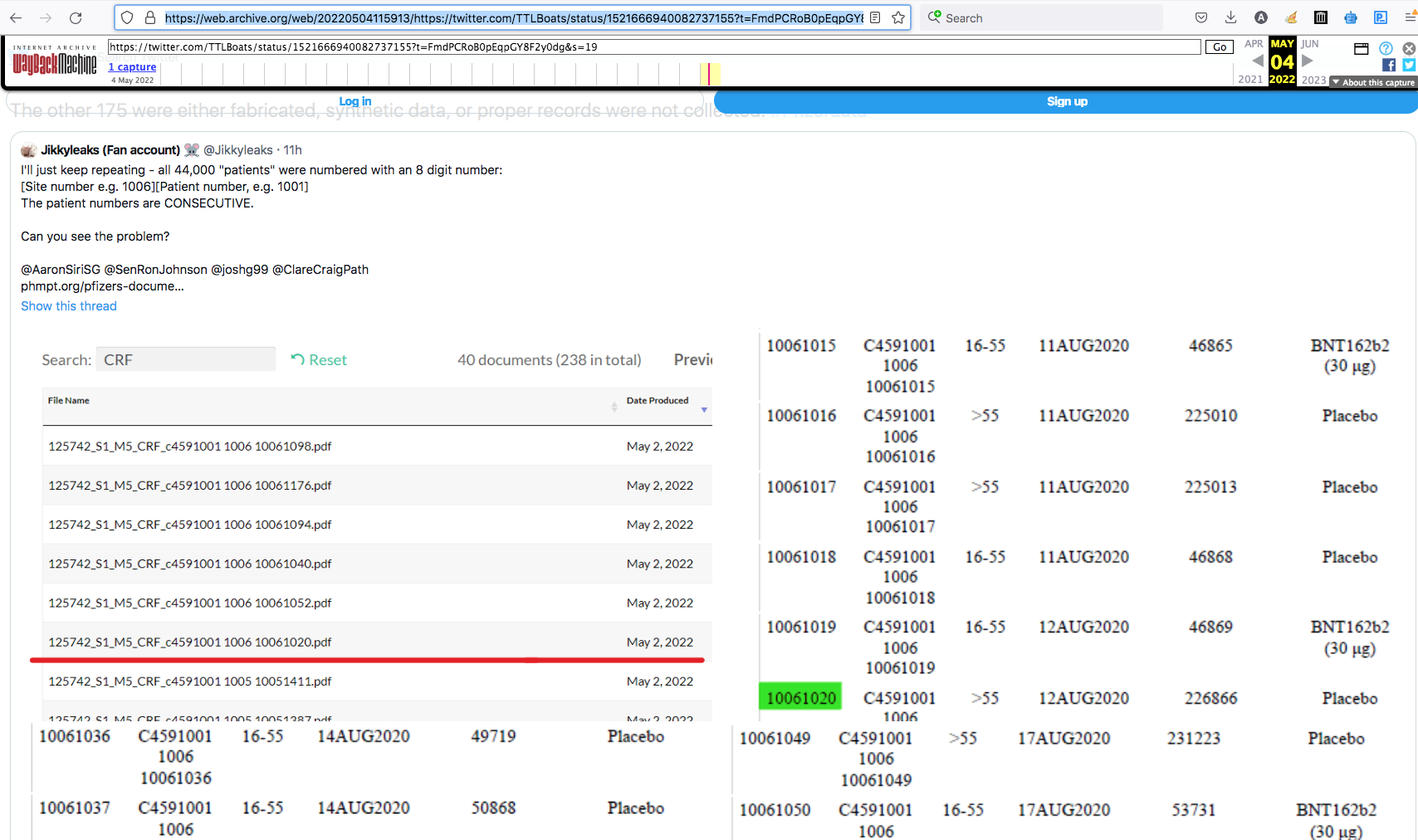
Don't Look Don't Find Excluded Studies
Dr. Paul Alexander May 2, 2022 18) Judicial Watch FOIA - Pfizer/BioNTech Study Found Lipid Nanoparticles Materials Outside Injection Site in Test Animals; MATCHES the Japanese biodistribution findings
The Pfizer records include a report, which was approved in February 2021, on the animal trials on the distribution of the Pfizer COVID vaccine in rat subjects, in a section titled “Safety Pharmacology,” the report notes, “No safety pharmacology studies were conducted with BNT162b2 [the BioNTech vaccine] as they are not considered necessary for the development of vaccines according to the WHO guideline (WHO, 2005).” Similarly, under “Pharmacodynamic Drug Interactions,” is “Nonclinical studies evaluating pharmacodynamic drug interactions with BNT162b2 were not conducted as they are generally not considered necessary to support development and licensure of vaccine products for infectious diseases (WHO, 2005).”…
This Pfizer report notes that when lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) “with a comparable composition,” to that used in the Pfizer COVID vaccine were injected into rats, “Total recovery (% of injected dose) of LNP outside the injection site was greatest in the liver and was much less in the spleen, adrenal glands, and ovaries.” … “in summary” … “the LNP distributes to the liver.” In the detailed analysis, the report states, “Over 48 hours, the LNP distributed mainly to liver, adrenal glands, spleen and ovaries, with maximum concentrations observed at 8-48 hours post-dose. Total recovery (% of injected dose) of LNP, for combined male and female animals, outside of the injection site was greatest in the liver (up to 18%) …”…
This same Pfizer/BioNTech study notes “No genotoxicity studies are planned for BNT162b2 [the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID vaccine] as the components of the vaccine constructs are lipids and RNA and are not expected to have genotoxic potential (WHO, 2005).” Similarly, “Carcinogenicity studies with BNT162b2 have not been conducted as the components of the vaccine construct are lipids and RNA and are not expected to have carcinogenic or tumorigenic potential.”…
Also included in the Pfizer records is a report, approved in January 2021, titled “Pharmacokinetics Tabulated Summary.” A table in the report shows the biodistribution of lipid nanoparticles containing mRNA used in the vaccine using rats as the clinical trial subjects reports LNPs accumulating after 48 hours, especially in the lymph nodes, ovaries, small intestine and spleen….
a November 4, 2020, report submitted to the FDA regarding the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine, the authors discuss the 2007 New Zealand rabbit study in which adenovirus-vectored vaccine is trialed, but note that “No pharmacokinetic or biodistribution studies have been conducted with AD26.COV2.S specifically.”
The report notes that metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetic interactions with other drugs were not studied in this trial because they are “Not applicable to vaccines.” It is also noted that “biodistribution studies have not been conducted with Ad26.COV2.S.” 19)
The Pfizer records include a report, which was approved in February 2021, on the animal trials on the distribution of the Pfizer COVID vaccine in rat subjects, in a section titled “Safety Pharmacology,” the report notes, “No safety pharmacology studies were conducted with BNT162b2 [the BioNTech vaccine] as they are not considered necessary for the development of vaccines according to the WHO guideline (WHO, 2005).” Similarly, under “Pharmacodynamic Drug Interactions,” is “Nonclinical studies evaluating pharmacodynamic drug interactions with BNT162b2 were not conducted as they are generally not considered necessary to support development and licensure of vaccine products for infectious diseases (WHO, 2005). 20)